前言
Java后端技术点
StringUtils常用API
学习时笔记(Linux)
学习时笔记(Git)
学习时笔记(Docker)
学习时笔记(Vue2+3)
面试宝典
学习时笔记(JavaScript)
1.JS基础:语法+流程控制
2.JS基础:数组+函数+对象
3.Web APIS:Dom获取+属性操作
4.Web APIS:Dom事件基础+进阶
5.Web APIS:DOM节点+移动端滑动
6.Web APIS:BOM操作+正则+阶段案例
7.JS进阶:作用域+解构+箭头函数
8.JS进阶:构造函数+数据常用函数+深入面向对象
9.JS进阶:高阶特性
10.ES6(上)
11.ES6(下)-ES9
12.ES10-ES13
学习时笔记(JavaWeb)
学习时笔记(Java)
学习时笔记(Python)
1.数组
查询
- 数组[下标]
新增
- 数组.push()——添加一个或多个元素到数组的末尾
- 数组.unshift()——添加一个或多个元素到数组的开头
let arr = ["马浩楠","程明辉"] // 新增 :添加到数组的结尾 并返回长度 length = arr.push("李泽","吴赛") document.write(length) // 新增:添加到数组的开头 并返回长度 newLength = arr.unshift("楠","22") document.write(arr) document.write(newLength)删除
- 数组.pop()——删除数组中的最后一个元素,并返回该元素值
- 数组.shift()——删除数组第一个元素,并返回该元素值
let arr = ["马浩楠","程明辉","李泽","吴赛"] // 1.pop删除最后一个元素,并返回删除的元素值 console.log(arr.pop()) // 吴赛 console.log(arr) // [ "马浩楠", "程明辉", "李泽" ] // 2.shift删除第一个元素,并返回删除的元素值 console.log(arr.shift()) // 马浩楠 console.log(arr) // [ "程明辉", "李泽" ] // 3.splice 删除指定元素 如果参数为一个,则表示该参数值位置后面全部删除 arr.splice(1,1) console.log(arr) //["程明辉"]
2.冒泡排序
let arr = [3,5,2,1,4]
console.log(arr.length)
for(let i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){
for(let j = i+1;j < arr.length;j++){
if(arr[i] < arr[j]){
let temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
}
}
}
console.log(arr)
3.函数
语法
function sayHi(){ document.write("hai~~") }函数传参
函数传参-默认值
- 形参:可以看作是变量,如果一个变量不给值,默认是什么
- undefined
function getSum(x = 0, y = 0){ document.write(x + y) } getSum() //结果是0,而不会是undefined + undefined = NaN getSum(1, 2) // 结果是3- 形参:可以看作是变量,如果一个变量不给值,默认是什么
函数返回值
细节补充
- 两个相同的函数后面的会覆盖前面的函数
- 在JS中,实参的个数和行参的个数可以不一致
- 如果行参过多,则会自动填补undefined
- 如果参数过多,多余的参数则会被忽略
- return作用
作用域:与Java一致
- 如果函数内部,变量没有声明,直接赋值,则为全局变量,不推荐这样做
匿名函数
- 函数表达式
let fn = function(x, y){ console.log(x + y) } fn(1, 2); // 3- 立即执行的匿名函数
- (function(){}())
- (function(){})()
// 2.匿名函数:第一种写法 【注意前后函数需要用;隔开】 (function () { let num = 10 console.log(num) // 10 })(); (function(){ let num = 20 console.log(num) // 20 })(); // 3.匿名函数:第二种写法 (function(x, y){ console.log(x + y) }(2, 1))
4.对象
声明语法
let 对象名 = {} let 对象名 = new Object()对象属性 —— 查
- 对象名.属性名
- 对象名["属性名"]
let person = { name: "马浩楠", age: 22, gender: "男" } console.log(person.name) console.log(person["age"])对象属性 —— 改/删
- 存在属性则改,不存在则为增
// 增 person.address = "河南省洛阳市" // 改 person.name = "浩楠"对象属性 —— 删
delete person.gender对象方法
let person = { name: "马浩楠", sayHi: function(){ document.write("Hello") } }遍历对象
let obj = { uname: "马浩楠", age: 22, gender: "男" } // 遍历对象 for(let k in obj){ console.log(obj[k]) }案例
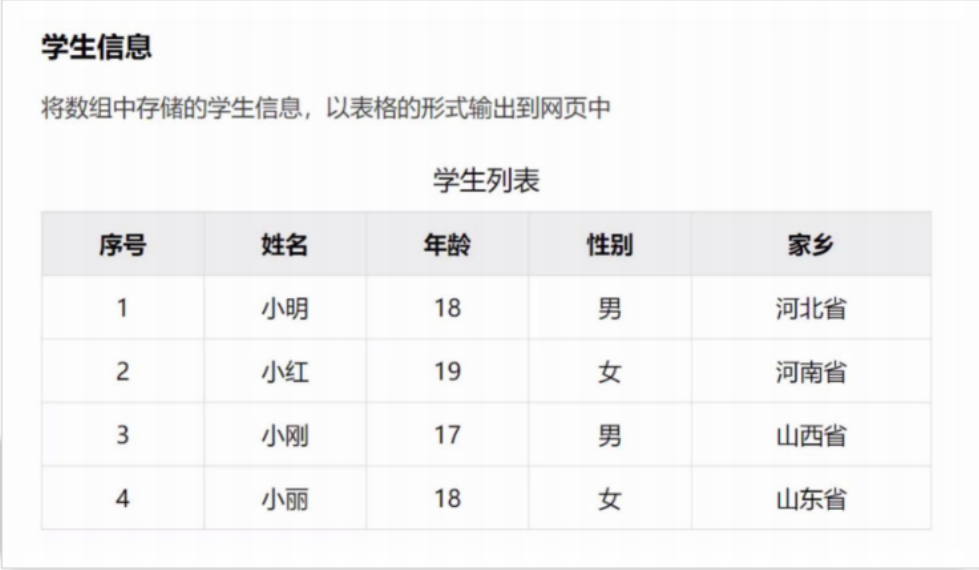
<style>
table {
margin:0 auto;
width:400px;
text-align: center;
height:200px
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>学生列表</h1>
<table cellspacing="0" border="1px">
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>家乡</th>
</tr>
<script>
let students = [
{name:"小明",age:18,gender:"男",hometown:"河北省"},
{name:"小红",age:19,gender:"女",hometown:"河南省"},
{name:"小刚",age:17,gender:"男",hometown:"山西省"},
{name:"小丽",age:18,gender:"女",hometown:"山东省"}
]
for(let i = 0;i < students.length; i++){
document.write(`
<tr>
<td>${i+1}</td>
<td>${students[i].name}</td>
<td>${students[i].age}</td>
<td>${students[i].gender}</td>
<td>${students[i].hometown}</td>
</tr>
`)
}
document.write("</table>")
</script>
</body>
</html>
内置对象
JavaScript内部提供的对象,包含各种属性和方法给开发者调用
- Math
// Math属性 console.log(Math.PI) // Math方法 // random 随机数 0-1之间 console.log(Math.random()) // 1.ceil()向上取整 console.log(Math.ceil(1,1)) // 2.floor()向下取整 console.log(Math.floor(1.1)) // 3.around()四舍五入 console.log(Math.round(1,4)) console.log(Math.round(1,5)) // 4.max()最大值 console.log(Math.max(1,2,3,4,5)) // 5.min()最小值 console.log(Math.min(1,2,3,5,6)) // 6.abs()取绝对值 console.log(Math.abs(-10))内置对象,生成任意范围随机数
// 左闭右开[0,1) ——可以取到0但取不到1 console.log(Math.random()) // 0~10之间的整数 console.log(parseInt(Math.random()*11)) // 5~10之间的整数 console.log(parseInt(Math.random()*6)+5) function getRandom(N, M){ return parseInt(Math.random()*(M - N +1))+N } console.log(getRandom(4,8))
5.数据类型
简单类型又叫做基本数据类型或者值类型,复杂类型又叫做引用类型
值类型
- 简单数据类型/基本数据类型,在存储时变量中存储的是值本身,因此叫做值类型:string、number、boolean、undefined、null
引用类型
- 复杂数据类型,在存储时变量中存储的仅仅是地址,因此叫做引用数据类型
栈内存
- 由操作系统自动分配释放存放函数的参数值、局部变量等。其操作方式类似于数据结构中的栈
简单数据类型存放在栈里面
堆内存
- 存放复杂类型(对象),一般由程序员分配释放,若程序员不释放,则由垃圾回收机制回收
引用数据类型放在堆内存中
