1.ES10:Object.fromEntries
可以将键值对(map)转换为对象
let arr = [["name","haonan"],["age",22]];
console.log(Object.fromEntries(arr)) // {name: "haonan",age: 22};
let m = new Map();
m.set("name","haonan");
m.set("age",22);
console.log(Object.fromEntries(m));
使用场景:获取路径参数
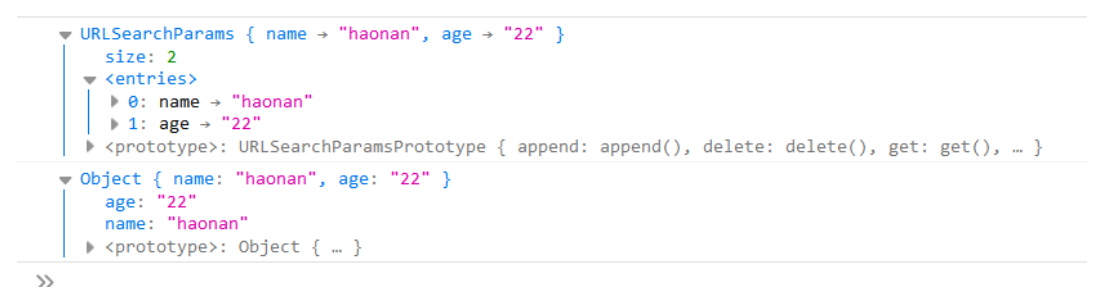
let str = "name=haonan&age=22"; let searchParams = new URLSearchParams(str); console.log(searchParams); console.log(Object.fromEntries(searchParams));
使用场景
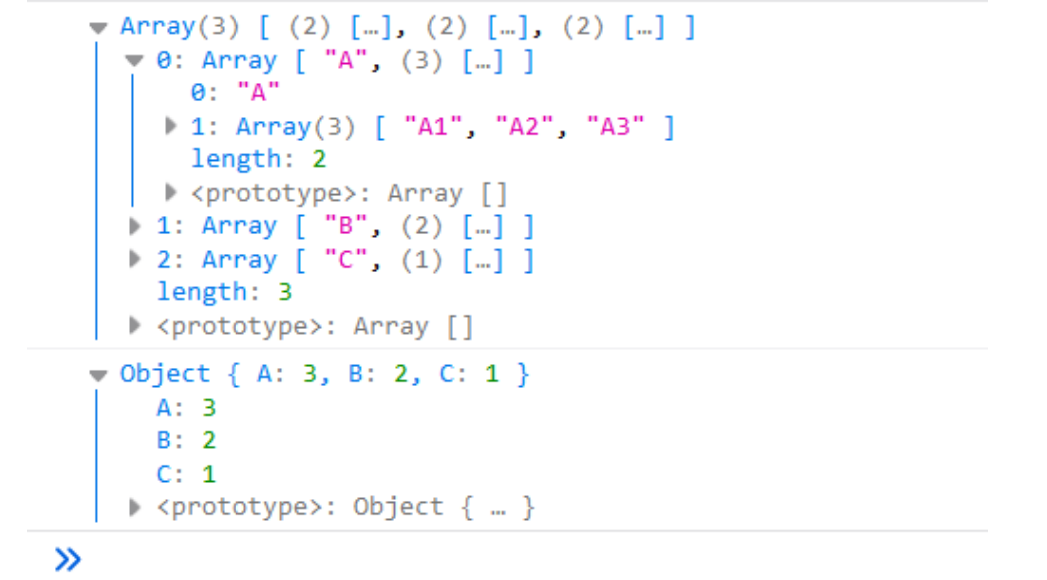
let obj = { "A":["A1","A2","A3"], "B":["B1","B2"], "C":["C1"] } // 将输出为 {"A":3,"B":长度} let arr = Object.entries(obj); console.log(arr); let newArr = arr.map(([key,value]) => { return [key,value.length]; }) console.log(Object.fromEntries(newArr));
2.ES10:其它新特性
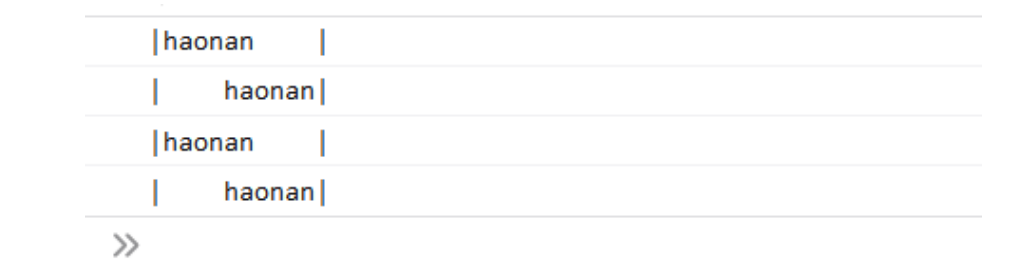
trimStart() 和 trimEnd()
trimStart() 和 trimEnd() 方法在实现与 trimLeft() 和 trimRight() 相同
let str = " haonan "; console.log("|"+str.trimStart(str)+"|"); console.log("|"+str.trimEnd(str)+"|"); console.log("|"+str.trimLeft(str)+"|"); console.log("|"+str.trimRight(str)+"|");
Symbol 对象的 description 属性
为 Symbol 对象添加了只读属性 description,该对象返回包含 Symbol 描述的字符串
let s = Symbol("haonan"); console.log(s.description); // haonan可选的catch
let pro1 = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){ setTimeout(() => { resolve("成功"); },30000) }) let pro2 = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){ setTimeout(() => { reject("失败"); },2000) }) async function test(){ try{ await Promise.race([pro1,pro2]); }catch { console.log("不需要错误信息"); } } test()
3.ES11:Promise.allSettled
Promise.allSettled() 方法返回一个在所有给定的 promise 都已经 fulfilled 或 rejected 后的 promise,并带有一个对象数组,每个对象表示对应的 promise 结果
let promises = [ajax("./1.json"),ajax("./2.json")];
Promise.allSettled(promises).then(results => {
// 过滤失败和成功的请求
result.filter(item => item.status === "fulfilled");
result.filter(item => item.status === "rejected");
})
4.ES11:module新增
动态导入 import()
标准用法的 import 导入的模块是静态的,会使得所有被导入的模块在加载时就被编译(无法做到按需编译,减低首页加载速度)。有些场景中可能需要根据条件导入模块,这时可以使用动态导入
- 1.js
console.log("1.js加载了"); export default{ name:"管理员模块" }- 2.js
console.log("2.js加载了"); export default{ name:"普通用户模块" }- html
<body> <button id="login"> login </button> <script type="module"> function login(){ return "管理员"; } let obtn = document.querySelector("#login"); obtn.addEventListener("click",function(){ let role = login(); console.log(role); render(role); }) async function render(role){ if(role === "管理员"){ // 加载 1.js,返回值为Promise对象s let res1 = await import("./1.js"); console.log(res1); }else{ let res2 = await import("./2.js"); console.log(res2); } } </script> </body>

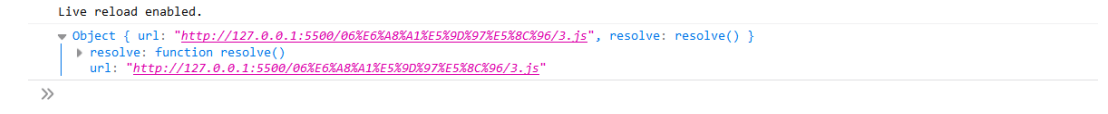
import.meta
该属性会返回一个对象,有一个 url 属性,返回当前模块的 url 路径【只能在模块内部使用】
<script type="model"> import obj from "./1.js" </script> // 1.js console.log(import.meta); export default{ }
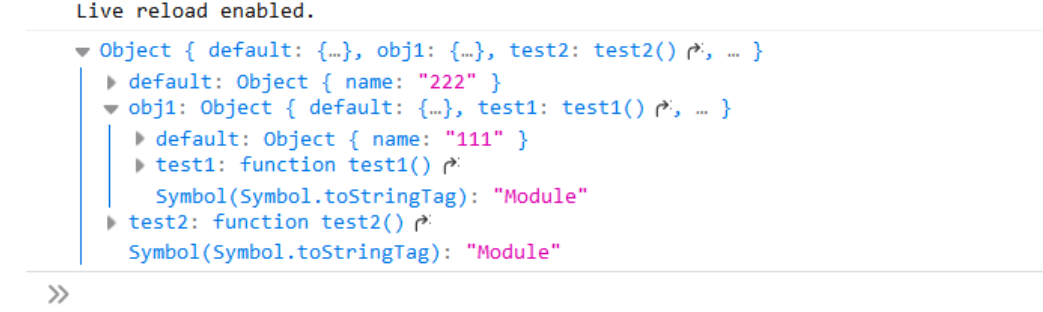
export * as obj from "module"
// 1.js export default { name: "111" } export function test1(){ } // 2.js export default{ name: "222" } export function test2(){ } export * as obj1 from "./1.js" // html <script type="module"> import * as obj from "./2.js" console.log(obj); </script>
5.ES11:字符串matchAll方法
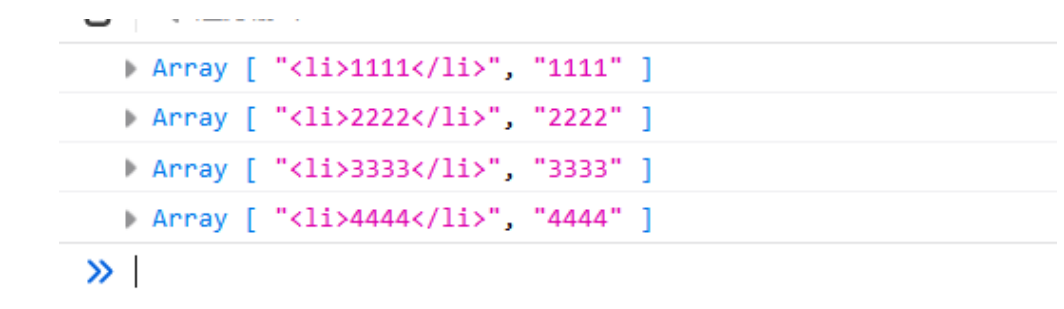
该方法返回一个包含所有匹配正则表达式的结果的迭代器,可以使用 for...of 遍历,或者使用展开运算符(...)和 Array.from 转换为数组
let str = `
<ul>
<li>1111</li>
<li>2222</li>
<li>3333</li>
<li>4444</li>
</ul>
`
let reg = /<li>(.*)<\/li>/g
for(let i of str.matchAll(reg)){
console.log(i)
}
6.ES11:BigInt
JS 能够准确的表示整数范围在 -2^53 到 2^53 之间(不含两个端点),超过这个范围,无法精确的表示这个值
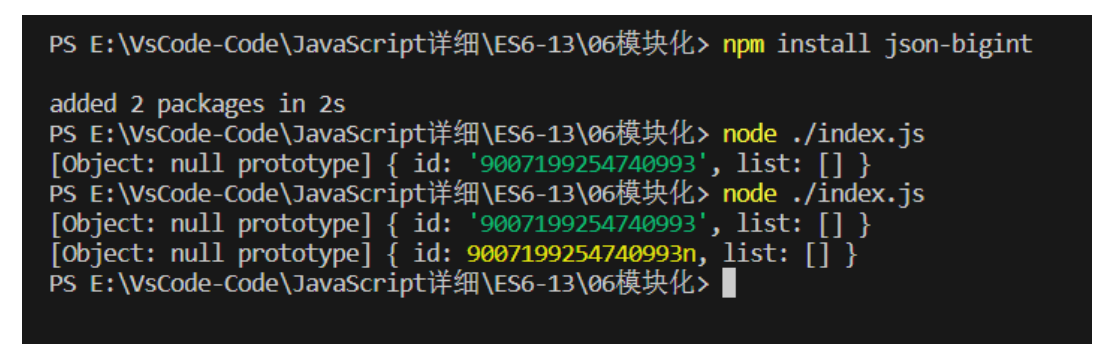
console.log(2**53); // 9007199254740992 let num1 = 123; let num2 = 123n; console.log(num1,num2); // 123 123n console.log(num1 == num2); // true console.log(num1 === num2); // false // BigInt 函数 console.log(BigInt(2)); // 2n // 运算 console.log(1n + 2n); // 3n使用场景:当后端穿过来的 id 值为:9007199254740993以上的值时,如何获取并处理
npm install json-bigint来下载,通过vue webpack等框架运行,或通过 node.js来运行
import JSONBigInt from "json-bigint" // 进行转字符串的方式 let JSONBigIntStr = JSONBigInt({ storeAsString: true}) // 进行转BigInt类型的方式 let JSONBigIntNative = JSONBigInt({ useNativeBigInt: true}) let josnStr = ` { "id": 9007199254740993, "list":[] } ` // 字符串 console.log(JSONBigIntStr.parse(josnStr)); // BigInt console.log(JSONBigIntNative.parse(josnStr));
7.ES11:其余新特性
GlobalThis
globalThis 提供了一个标准的方式来获取不同环境下的全局 this 对象(也就是全局对象自身)。不像 window 或者 self 这些属性,它确保可以在有无窗口的各种环境下正常工作。所以,可以安心的使用 globalThis,不必担心运行环境。
空值合并运算符
?? 是一个逻辑运算符。当左侧操作数为 null 或 undefined 时,返回其右侧的操作数,否则返回左侧
console.log(null ?? "haonan"); // haonan console.log(undefined ?? "haonan"); // haonan console.log(0 || "haonan"); // 0 console.log(0 ?? "haonan"); // haonan- ?? 和 || 两者区别
区别在于当左侧 值为 '' 或者 0 的时候,依然返回左侧值
而 || 会对左侧的数据进行 boolean 类型转换,所以返回为右侧值
可选链操作符
可选链前面的值如果是 null 或 undefined,则不再执行后面的,之前返回的可选链前面的值
let obj = { name: "haonan", introduction: 0, // location:{ // city: "luoyang" // } } console.log(obj && obj.location && obj.location.city); // undefined console.log(obj?.location?.city); // undefined
8.ES12:新特性
逻辑赋值操作符
??=、&&=、||=
let a = true; let b = false; a ||= b; console.log(a); // true a &&= b console.log(a); // false数字分隔符
为了方便程序员看代码而存在的,如果数字比较大,那么看起来会一目了然
let num1 = 123456789; let num2 = 123_456_789; console.log(num1 === num2); //truereplaceAll
所有匹配都会被替代项替换,模式可以是字符串或正则表达式,并返回一个全新的字符串
const str = "I wish to wish the wish you wish to wish, but if you wish the wish the witch wishes, I won't wish the wish you wish to wish. "; const newStr = str.replaceAll("wish", "***"); console.log(newStr); // I *** to *** the *** you *** to ***, but if you *** the *** the witch ***es, I won't *** the *** you *** to ***.Promise.any
只要参数实例有一个变成 fulfilled 状态,包装实例就会变成 fulfilled 状态;如果所有参数实例都变成 rejected 状态,包装实例就会变成 rejected 状态
- Promise.any() 和 Promise.race() 方法类似,不同在于,Promise.nay() 不会因为某个 Promise 变成 rejected 状态而结束,必须等到所有参数 Promise 变成 rejected 状态才会结束
9.ES12:WeakRef、FinalizationRegistry
WeakSet
let obj = { name: "haonan" } let s1 = new Set(); s1.add(obj); let s2 = new WeakSet(); s2.add(obj); obj = null; console.log(s1); // 依然存在obj console.log(s2); // 不存在- 只能是复杂类型
- 不存在引用计数,所以当obj为null时,虽然存在 WeakSet(),但还是会被垃圾回收机制回收
- size,for 不能使用
WeakMap
- 同WeakSet
WeakRef
在一般情况下,对象的引用是强引用的,这意味着只要持有对象的引用,它就不会被垃圾回收,只有当该对象没有任何的强引用时,垃圾回收才会销毁该对象并且回收该对象所占的内存空间。而 WeakRef 允许保留对另一个对象的弱引用,而不会阻止被弱引用对象被垃圾回收
let target = {}; let wr = new WeakRef(target);WeakRef 实例对象存在 deref() 方法,如果原始对象存在,该方法返回原始对象,如果原始对象已经被垃圾回收机制回收,该方法返回 undefined
let like = new WeakRef(document.querySelector("#like")); let myMap = new WeakMap(); myMap.set(like.deref(),{click:0}); like.deref().addEventListener("click",function(){ myMap.get(like.deref()).click++; }) setTimeout(() => { document.body.removeChild(like.deref()); },3000)FinalizationRegistry
清理器注册表功能 FinalizationRegistry,用来指定目标对象被垃圾回收机制清除后,所要执行的回调函数
let registry = new FinalizationRegistry(data => { console.log("销毁了",data); }) let obj = { name:"haonan" } registry.register(obj,"111"); obj = null; // 当被垃圾回收机制回收的时候,则会触registry发回调函数 // 取消注册 registry.unregister(obj);
10.ES13:新特性
类的固定值简写
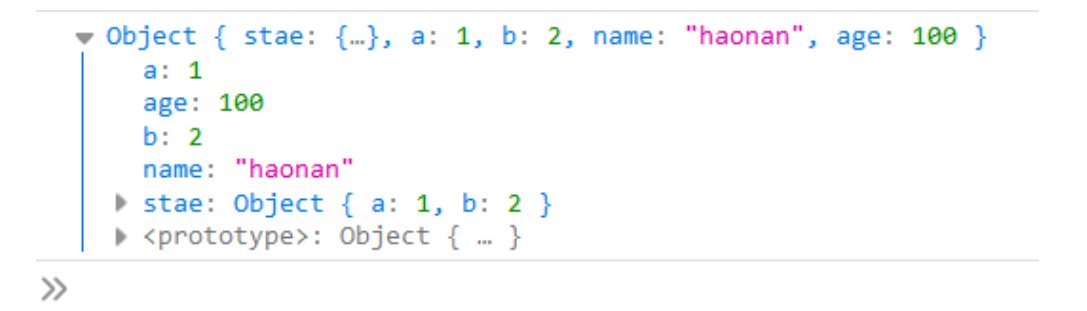
class Person{ stae = { a:1, b:2 } a = 1; b = 2; constructor(name,age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; // this.stae = { // a:1, // b:2 // } } } let obj = new Person("haonan",100); console.log(obj);
私有属性和方法
class Cache{ #obj = {}; get(key){ return this.#obj[key]; } set(key,value){ this.#obj[key] = value; } } let cache = new Cache(); console.log(cache.#obj); // 报错,访问不到 cache.set("name","haonan"); cache.get("name"); // haonan静态成员的私有属性和方法
可以给类定义静态成员和静态私有函数。类的静态方法可以使用 this 关键字访问其它的私有或者共有静态成员
class Cache{ static #count = 0; static getCount(){ return this.#count; } } let cache = new Cache(); console.log(cache.#count); // 报错,无法访问 console.log(cache.getCount()); // 0静态代码块
可以定义任意多的静态代码块,这些代码块会穿插在它们之间的静态成员变量一起按照定义的顺序在类初始化的时候执行一次,也可以使用 super 关键字来访问父类的属性
class Cache{ static obj = new Map(); static { this.obj.set("name","haonan"); this.obj.set("age",22); } static { console.log(this.obj); } }使用 in 来判断某个对象是否拥有某个私有属性
class Cache{ #obj = {}; get(key){ return this.#obj[key]; } set(key,value){ this.#obj[key] = value; } hasObj(){ return #obj in this; } } let cache = new Cache(); console.log(cache.hasObj());支持在最外层写 await
- 1.js
function ajax(){ return new Promise(resolve => { setTimeout(() => { resolve("data"); },3000); }) } let data = await ajax(); export default{ name: "ModuleA", data }- html:结合动态导入使用
console.log("开始"); let moduleA = await import("./1.js"); console.log(moduleA);at函数来索引元素
let arr = ["mahaonan","chengminghui","wusai","lize"]; // 取第一个 console.log(arr[1]); console.log(arr.at(1)); // 取倒数第一个 console.log(arr[arr.length-1]); console.log(arr.at(-1)); // 取倒数第二个 console.log(arr[arr.length-2]); console.log(arr.at(-2)); // string 字符串 同理正则表达式的开始和结束索引
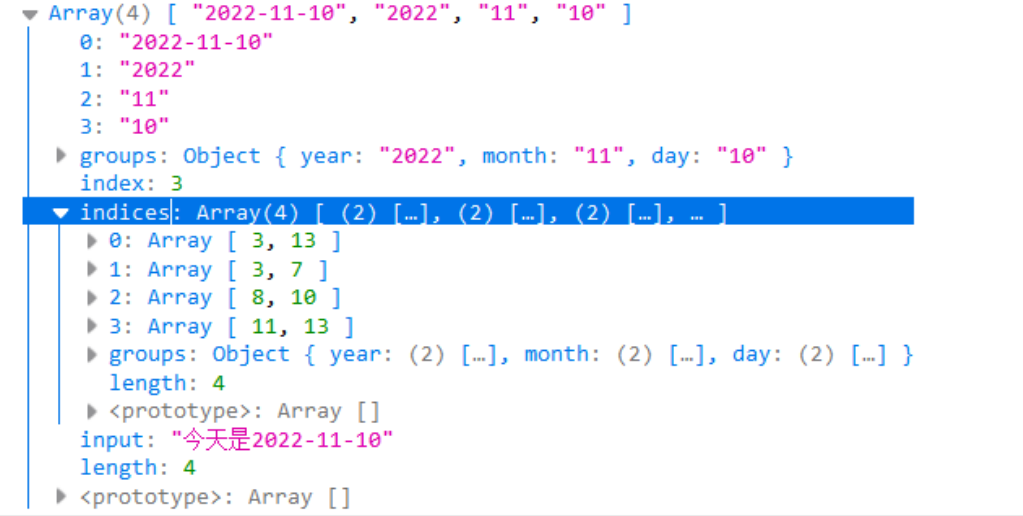
let str = "今天是2022-11-10"; let reg = /(?<year>[0-9]{4})-(?<month>[0-9]{2})-(?<day>[0-9]{2})/d let res = reg.exec(str); console.log(res);
findLast() 和 findLastIndex() 函数
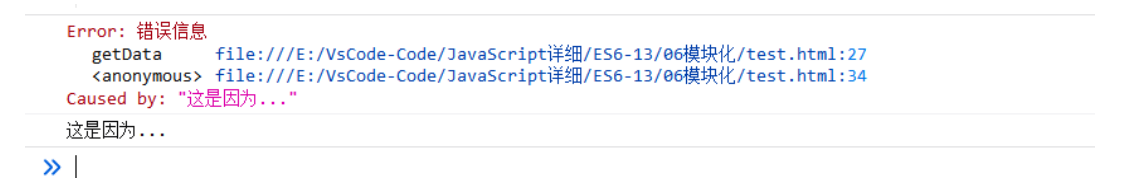
let arr = [11,12,13,14,15]; let res1 = arr.find(item => item%2 === 0) console.log(res1); // 12 let res2 = arr.findLast(item => item%2 === 0); console.log(res2); // 14 let res3 = arr.findIndex(item => item%2 === 0); console.log(res3); // 1 let res4 = arr.findLastIndex(item => item%2 === 0); console.log(res4); // 3Error对象的Cause属性
Error 对象多了一个 cause 属性来指明错误出现的原因。这个属性可以帮助我们为错误添加更多的上下文信息,从而帮助使用者们更好的定位错误
function getData(){ try{ console.log(haonan); }catch(e){ throw new Error("错误信息",{cause:"这是因为..."}); } } try{ getData(); }catch(e){ console.log(e); console.log(e.cause); }